nalidixic acid

CLINICAL USE
Antibacterial agent
DOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
600–900 mg every 6 hours
PHARMACOKINETICS
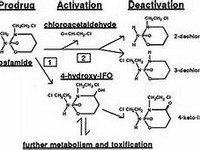
Molecular weight :232.2 %Protein binding :93–97 %Excreted unchanged in urine : 11–33 (80–90% as inactive metabolites) Volume of distribution (L/kg) :0.47–0.55half-life – normal/ESRD (hrs) :6–8/21 DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
20 to 50 : Dose as in normal renal function 10 to 20 : Dose as in normal renal function <10 : Avoid. See ‘Other Information’ DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
CAPD :Unlikely to be dialysed. Dose as in GFR <10 mL/min HD :Unlikely to be dialysed. Dose as in GFR <10 mL/minHDF/high flux :Unlikely to be dialysed. Dose as in GFR <10 mL/minCAV/VVHD :Unknown dialysability. Dose as in normal renal function IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsAnalgesics: increased risk of convulsions with NSAIDsAnticoagulants: anticoagulant effect of coumarins enhancedCiclosporin: increased risk of nephrotoxicityAntimalarials: manufacturer of artemether with lumefantrine advises avoid concomitant useTheophylline: possibly increased risk of convulsions ADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
– Route
Oral Rate of Administration
–Comments
– OTHER INFORMATION
Avoid in severe renal impairment because the concentration in the urine is inadequate, and risk of monoglucuronide metabolite toxicity.
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home